
Alan Turing will appear on the new £50 note which will be issued from June 23, the Bank of England has confirmed.
The release coincides with what would have been the code-breaker's 109th birthday.
The polymer £50 note contains advanced security features. The note, like the latest £20, incorporates two windows and a two-colour foil, making it very difficult to counterfeit, the Bank said.
There is also a hologram image which changes between the words Fifty and Pounds when tilting the note from side to side.
Alan Turing was born in London in 1912, but spent several of his early years living in St Leonards.
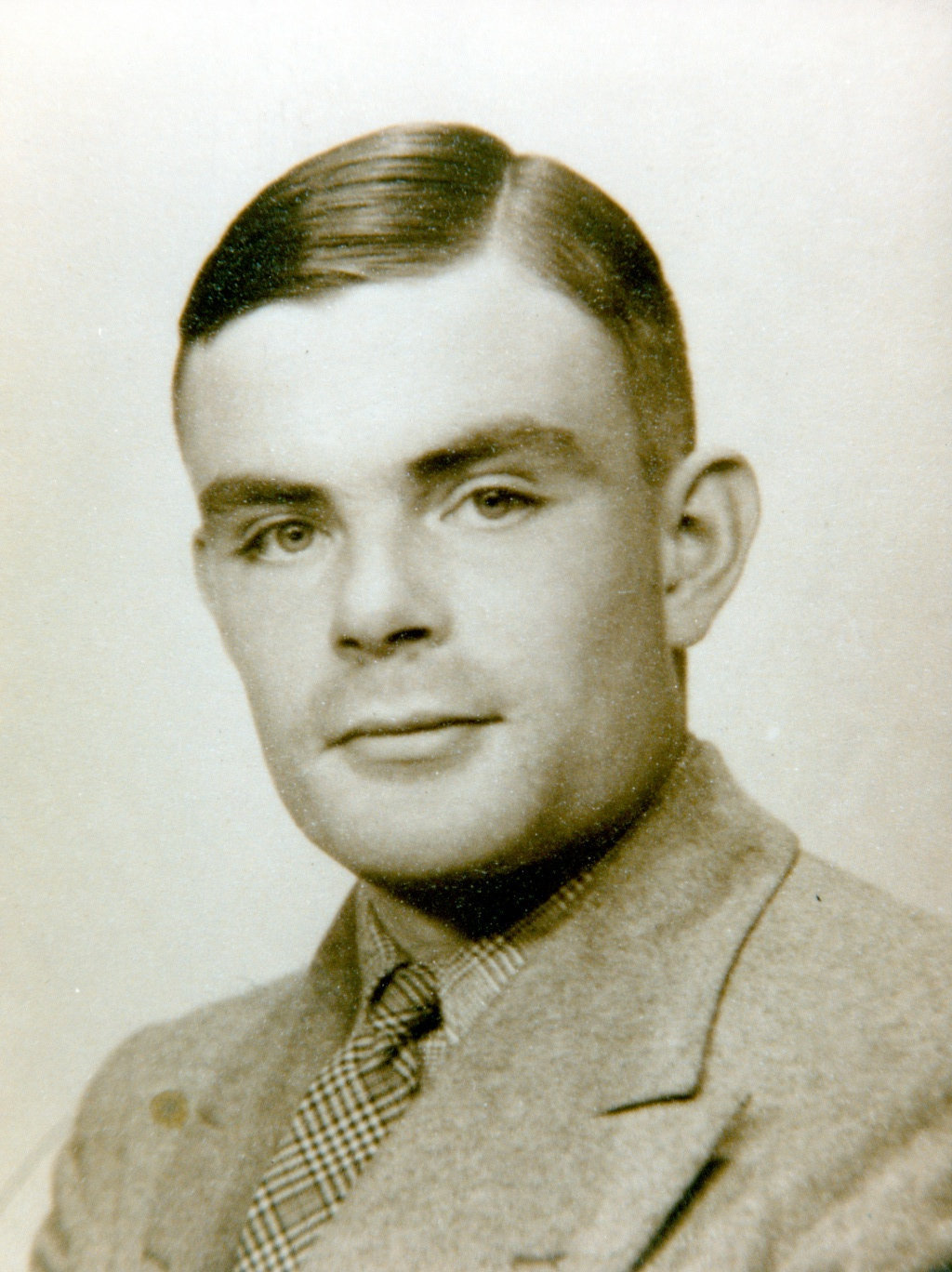

Alan Turing. Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office
He was a pioneer of modern computing and hugely instrumental in breaking the German Naval Enigma cipher in 1942, at Bletchley Park - cyber and intelligence agency GCHQ's wartime home.
Following the announcement that Mr Turing will feature on the new £50 note, GCHQ has created its "toughest puzzle ever".
Officials say their new treasure hunt involves 12 puzzles and "might even have left him scratching his head".
Director of the cyber and intelligence agency Jeremy Fleming described Mr Turing becoming the first gay man to appear on a banknote as confirming his status as "one of the most iconic LGBT+ figures in the world".
Mr Fleming said: "Alan Turing's appearance on the £50 note is a landmark moment in our history.
"Not only is it a celebration of his scientific genius, which helped to shorten the war and influence the technology we still use today, it also confirms his status as one of the most iconic LGBT+ figures in the world.
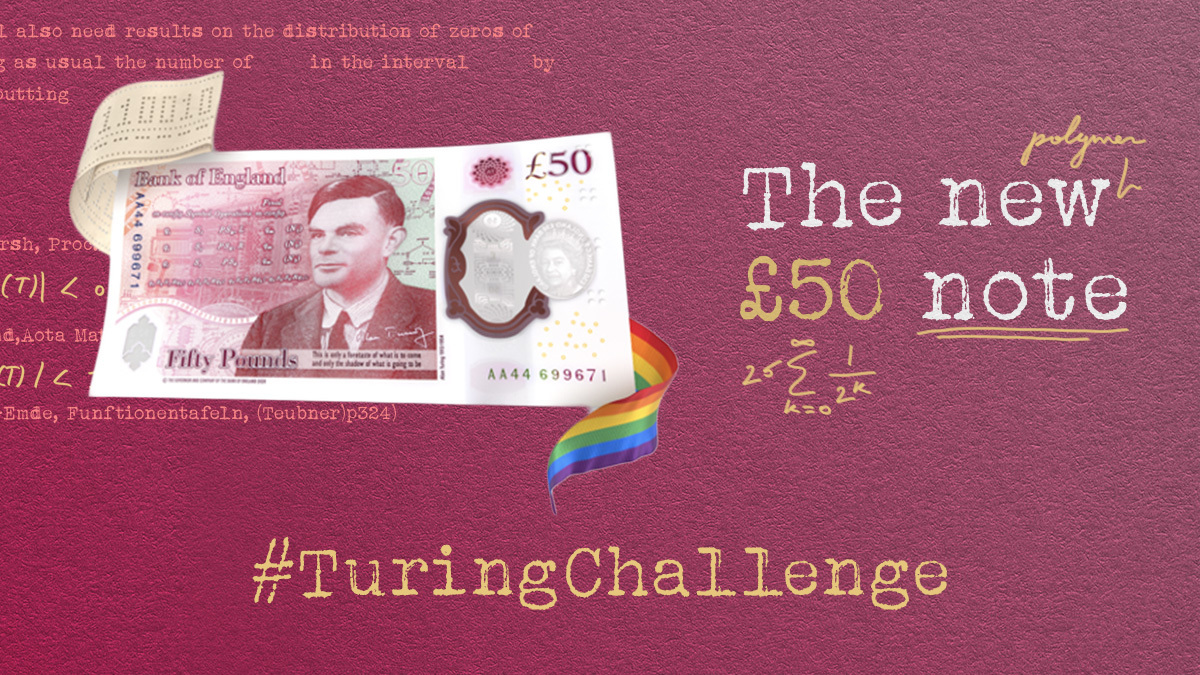
The new £50 note will feature Alan Turing
"Turing was embraced for his brilliance and persecuted for being gay.
"His legacy is a reminder of the value of embracing all aspects of diversity, but also the work we still need to do to become truly inclusive."
The puzzles are based on the unique design elements of the new banknote, such as the technical drawings for the British Bombe, the machine designed by Mr Turing to break Enigma-enciphered messages.
GCHQ officials said the full challenge could take an experienced puzzler seven hours to complete.
Colin, a GCHQ analyst and its chief puzzler, said: "Alan Turing has inspired many recruits over the years to join GCHQ, eager to use their own problem-solving skills to help to keep the country safe.
"So it seemed only fitting to gather a mix of minds from across our missions to devise a seriously tough puzzle to honour his commemoration on the new £50 note.
"It might even have left him scratching his head - although we very much doubt it."
Mr Turing joined the Government Code and Cypher School - GCHQ's wartime name - in 1938 to help with the code-breaking effort during the Second World War, working alongside Gordon Welchman.

Alan Turing
In January 1940, Mr Turing had a meeting in Paris with Polish counterparts, who gave him the insights he needed to design the Bombe.
The combination of the Bombe and the brilliant minds and perseverance of those working at Bletchley Park led to the breaking of Enigma.
In January 1952, Mr Turing was prosecuted for "indecency" over his relationship with another man in Manchester, and was given a choice between imprisonment and probation on condition of undergoing hormone treatment.
In 1954, Mr Turing took his own life.



Comments: Our rules
We want our comments to be a lively and valuable part of our community - a place where readers can debate and engage with the most important local issues. The ability to comment on our stories is a privilege, not a right, however, and that privilege may be withdrawn if it is abused or misused.
Please report any comments that break our rules.
Read the rules hereLast Updated:
Report this comment Cancel